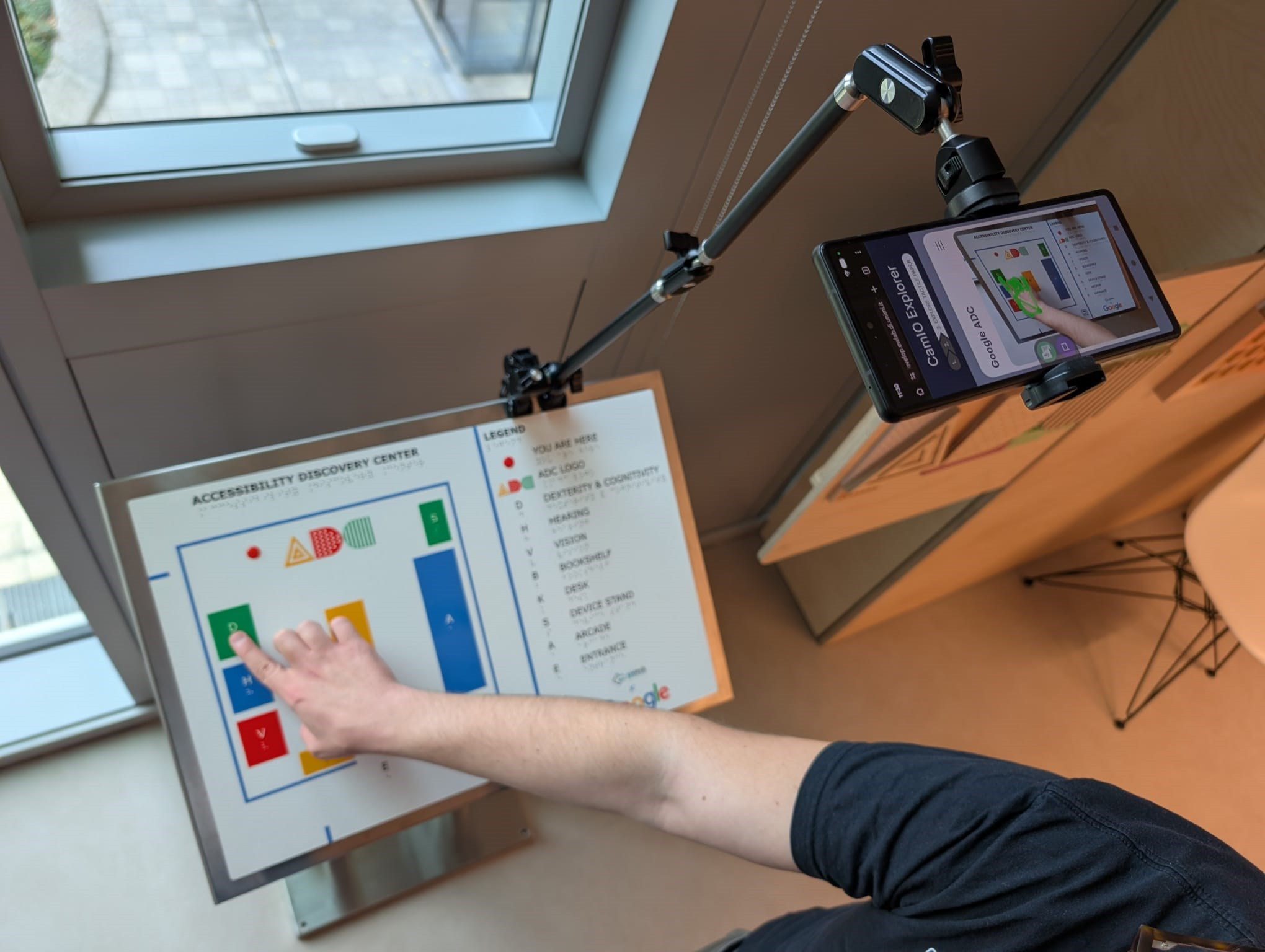
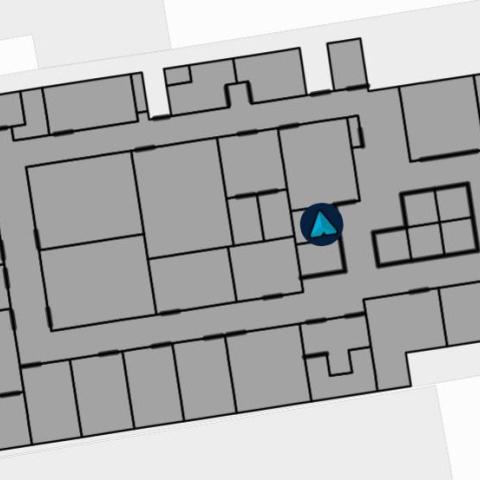
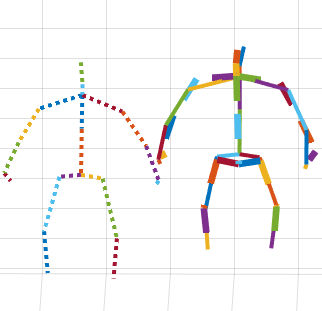Interactive Tactile Map at Google ADC Milan
This is an installation of the CamIO project that adds interactivity to a tactile map of the Google Accessibility Discovery Center in Milan, Italy.
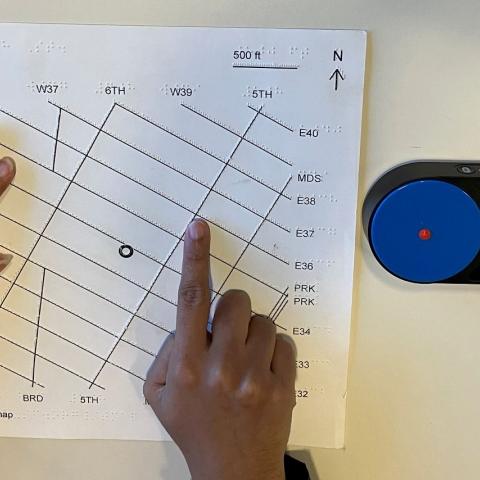
Audiom Map of Smith-Kettlewell
An Audiom map of the main Smith-Kettlewell building at 2318 Fillmore St., San Francisco has been created by Brandon Biggs. This is an audio-visual map that allows users to explore a detailed map of the building with or without vision. The map runs in any browser and is available to anyone who visits the building.
Crowd-Sourced Description for Web-Based Video (CSD)
The Descriptive Video Exchange Project (funded by the National Eye Institute of the National Institutes of Health, (grant # R01 EY020925-01) focuses on crowd-sourced techniques for describing DVD media. CSD will expand DVX to include Internet-based media such as YouTube, iTunes U, and other streamed video found on a wide variety of web sites. Many streamed Internet-based video sources provide well-defined, public APIs for accessing all the information DVX requires. Using these APIs will allow the VDRDC to expand DVX to include streamed content so that seamless, simple, crowd-sourced descriptions can be added to Internet-based video by volunteers or professionals anywhere.
MapIO: a Gestural and Conversational Interface for Tactile Maps
For individuals who are blind or have low vision, tactile maps provide essential spatial information but are limited in the amount of data they can convey. Digitally augmented tactile maps enhance these capabilities with audio feedback, thereby combining the tactile feedback provided by the map with an audio description of the touched elements. In this context, we explore an embodied interaction paradigm to augment tactile maps with conversational interaction based on Large Language Models, thus enabling users to obtain answers to arbitrary questions regarding the map. We analyze the type of…
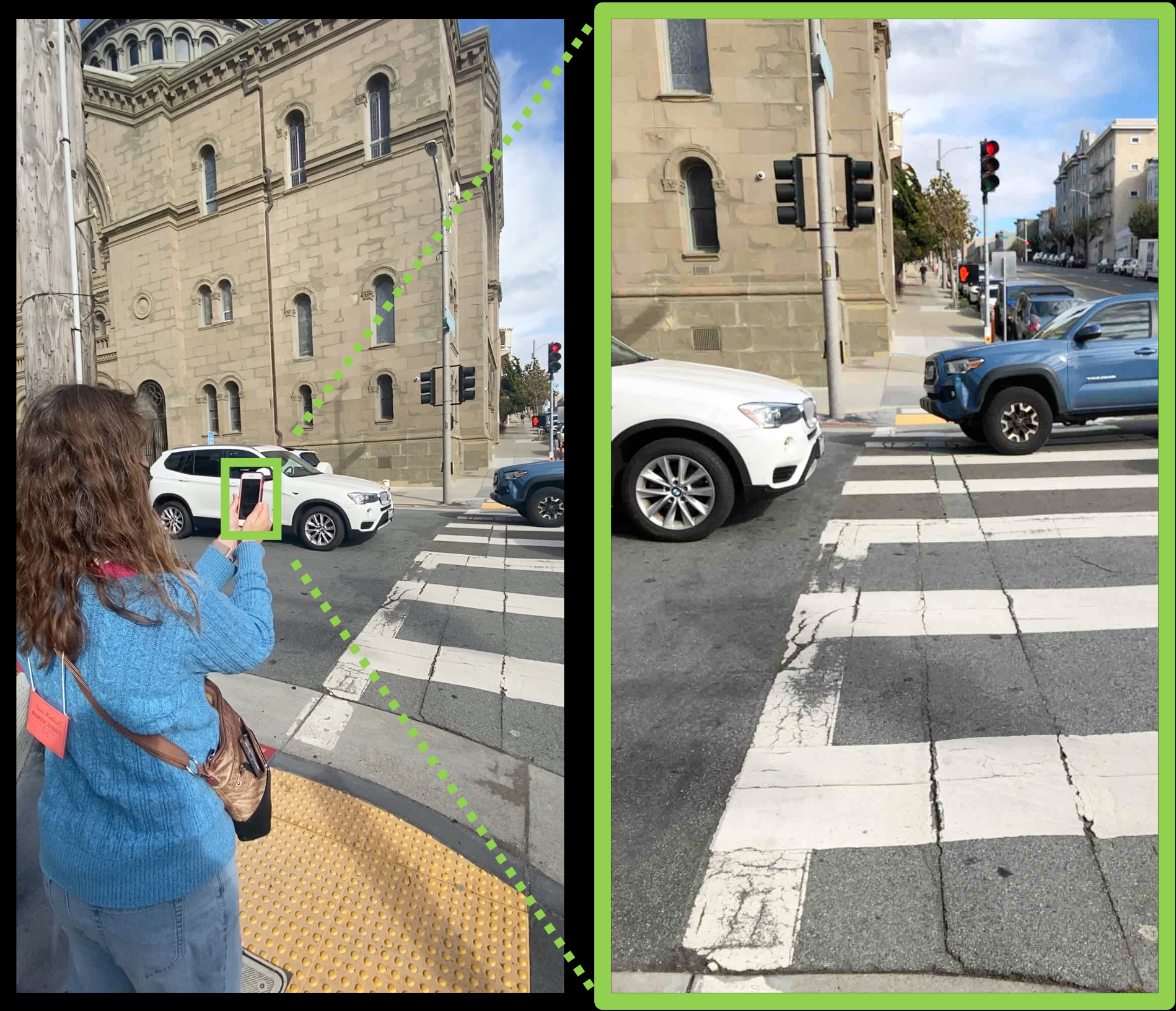
Using VR to Help Train Visually Impaired Users to Aim a Camera
People with visual impairments increasingly rely on camera-enabled smartphone apps for tasks like photography, navigation, and text recognition. Despite the growing use of these applications, precise camera aiming remains a significant challenge. This project explores the impact of virtual reality (VR) exploration in the context of learning to use a camera-based app. So far we have studied this approach in the context of training a visually impaired person to use walk-light detector app at traffic intersections.
Smith-Kettlewell Summer Institute
The Smith-Kettlewell Summer Institute program is a multi-year, learning opportunity designed to provide training for blind and visually impaired students, recent graduates, and early career researchers interested in data skills that will enhance Science, Technology, Engineering and Math (STEM) jobs within industry, government, non-profit organizations or academia.
In today’s research climate, individuals are expected to have many skills at their fingertips. Often researchers are required to build software and hardware environments to run studies, to gather and analyze data and to prepare…
Mobility and Fall Risk in Central Visual Field Loss
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is the most common cause of vision loss in the developed world. Central visual field loss due to diseases such as AMD is a large and growing problem. It is also associated with higher risk of falls and, therefore injury. Although much has been done to understand visual limitations associated with this condition, one of its most dangerous and poorly understood outcomes is the increase in the risk of falls, which can be debilitating and even deadly, especially in the age group most affected by AMD. The exact reasons for the increased fall risk are unknown…
Empowering Data Vision: Data Science Course for Blind Individuals using Python
Call for Participation:
Second Smith-Kettlewell Summer Research Institute, “Empowering Data Vision: Data Science Course for Blind Individuals using Python”
The Smith-Kettlewell Eye Research Institute, the University of Michigan and the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign are delighted to present our second on-line course dedicated to data science for blind individuals.
Overview:
This course, “Empowering Data Vision: A Data Science Course for Blind Individuals using Python,” will teach blind individuals the basics of using Python to interact with datasets. The course will be offered on…